
#Resistors in parallel formula series
This is because there is only one path for current flow in a series circuit. The amount of current in a series circuit is the same through any component in the circuit. The potential difference across them will be different if they have different resistances. The two resistors have the same current through them. In a series circuit, the total resistance across all of the components (the ‘net resistance’) increases as more components are added. … Adding more parallel resistances to the paths causes the total resistance in the circuit to decrease. For one, the total resistance of a Parallel Circuit is NOT equal to the sum of the resistors (like in a series circuit). The parallel circuit has very different characteristics than a series circuit. Why is resistance different in series and parallel? The voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the size of the resistor. Voltage applied to a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops. The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the sum of individual resistances. In a parallel circuit, all of the resistor leads on one side of the resistors are connected together and all the leads on the other side are connected together. In a series circuit, the output current of the first resistor flows into the input of the second resistor therefore, the current is the same in each resistor. There are four factors affecting resistance which are Temperature, Length of wire, Area of the cross-section of the wire, and nature of the material. Resistance is the property of the material that restricts the flow of electrons. What are the factors affecting the resistance?
Analog multimeters and digital multimeters employ the measurement principle of Ohm’s Law to measure resistance. As a result, a circuit’s resistance value can be determined if the current and voltage measured values are known. Resistance can be calculated by measuring the current and voltage using Ohm’s Law.

Using Ohm’s Law to calculate the resistance, we haveĪpplying this formula on separate resistors- I 1 = V/R 1

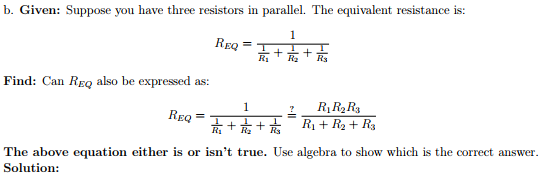
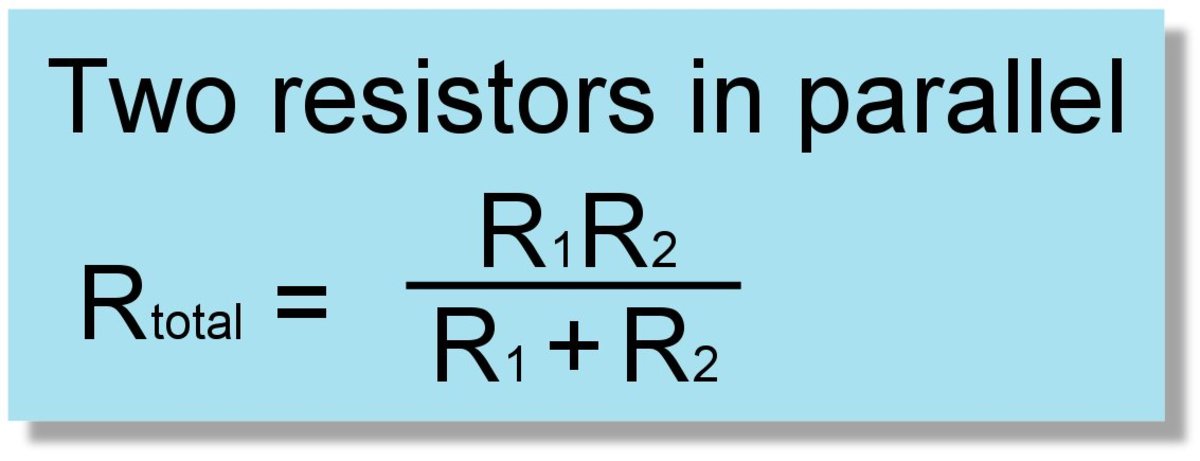
In Parallel arrangement, if four resistors are joined in a circuit, then the total current I, will be calculated by summing up the separate currents flowing through each branch of the arrangement. Read more : Important Formula in electricity In a parallel circuit, any component or resistor can be easily disconnected or connected and that will not affect the other elements of the circuit. So, the resistors in a parallel combination would have a Common Voltage in them. While there are many paths for the current to flow, all branches of the parallel circuit may not have the same amount of current flowing through them. In the case of a Parallel Combination in an electric circuit, the current gets divided itself and flows through different branches, and meets at a common point where the branches meet. The total amount of resistance in the circuit is the total amount of individual resistances.Ĭalculation of Resistance in Parallel Combination The total resistance in the circuit will be: In the case of the condition where there are ‘n’ numbers of resistors: If the number of resistors present in a circuit is 4, then the according to the Ohm’s Law: In a series combination, if any kinds of fault or damage take place, it would result in the turning off of the entire circuit. The circuit construction in series combination is much simpler than Parallel combination circuits. V = IR where V stands for the Potential Drop. There is always a chance of a drop of voltage in it.Īgain we can use Ohm’s Law to explain the series combination in order to calculate the resistance in the circuit, i.e. In the case of a series combination, we have the resistors set in series, hence the flow of current in them will pass through the resistors one after another. Calculation of Resistance in Series Combination


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
